Dog Eye Anatomy Carlson Stock Art
When considering the anatomy of the eye, it is important to first consider the orbit as a whole.. In the dog, the upper eyelid contains >2 rows of cilia, whereas the cat does not have any. Instead the first row of hairs on the skin are adapted for the same purpose. There are two types of gland associated with the cilia; Moll (which are.
Dog eye anatomy Quiz
The eyes of animals, including dogs' eyes , function much like yours. Animals also develop many of the same eye problems that people can have, including cataracts, glaucoma, and other problems. It is important for your dog to receive good eye care to protect its sight and allow it to interact comfortably with its environment.
Diseases of the Eye Veterian Key
1 KEEP YOUR DOG'S EYES HEALTHY: OVERVIEW 1. Eyes respond well to natural health prevention methods, so keep them healthy with nutrition, exercise, care of the immune system, and avoidance of toxins and stressors. 2. Use alternative therapies - by themselves or in combination with conventional medicine - to treat short- or long-term eye problems.
Dog Eyelid Anatomy
Dog eyes are made up of a cornea, iris, pupil, lens, retina, and sclera. They also have an upper and lower eyelid and a third eyelid on the outside of the eye for protection. Rods and cones are how images and light are processed and important for vision. Let's take a closer look at how each of these works. Cornea
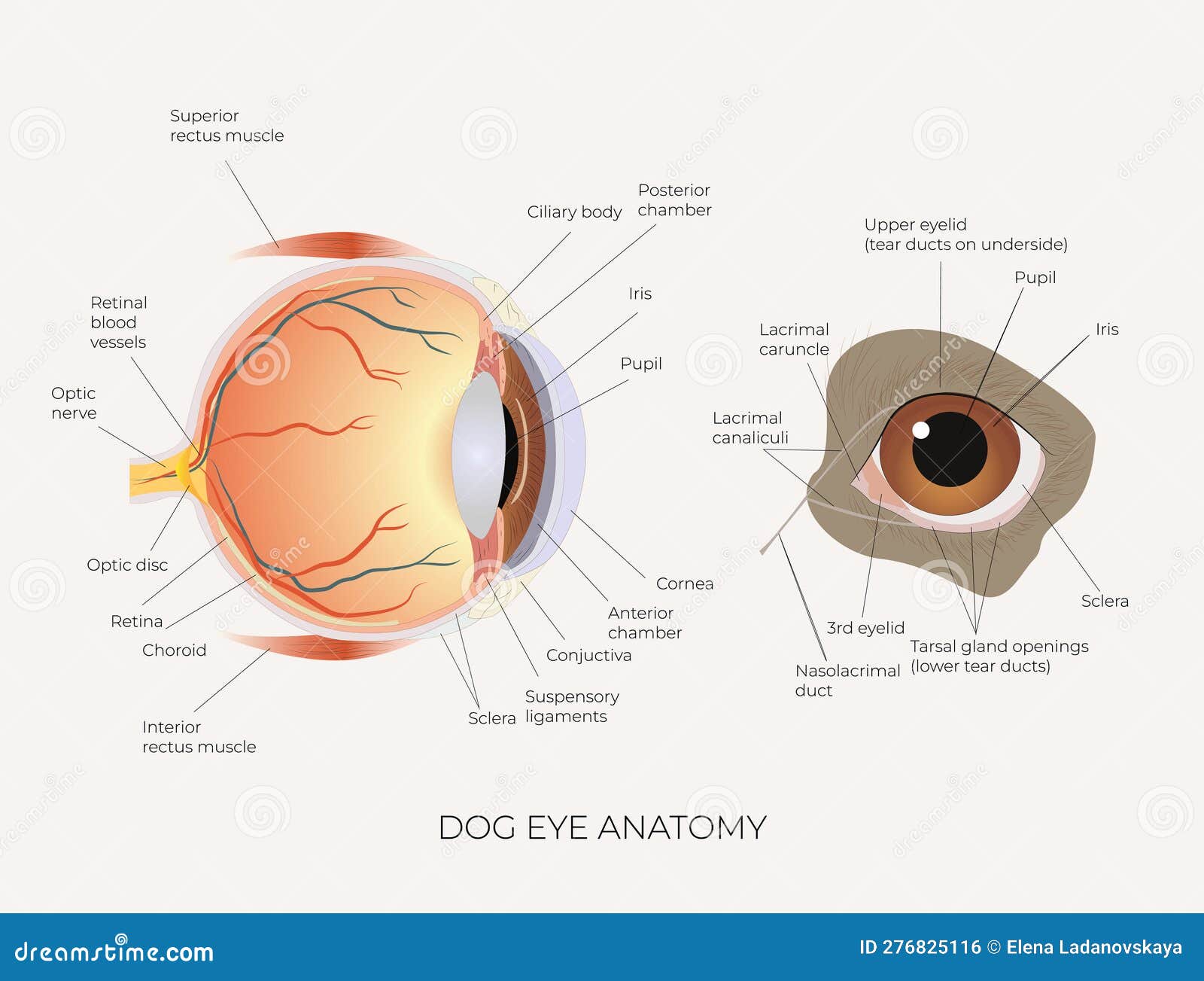
Dog Eye Anatomy Science Education Poster Stock Vector Illustration of medicine, zoology 276825116
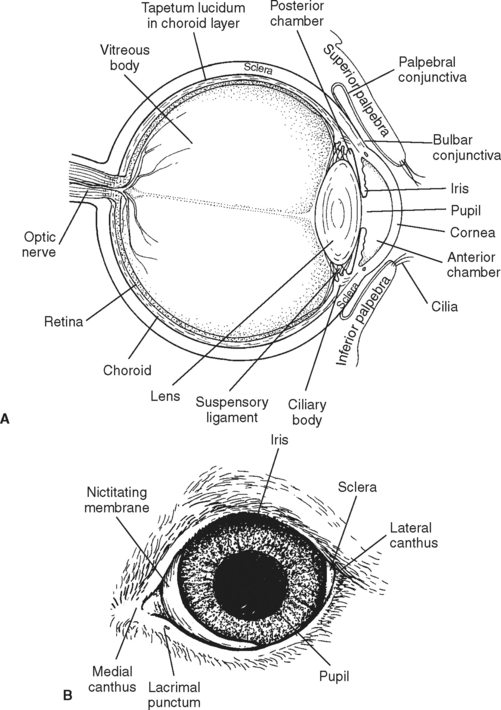
Dog eye anatomy Dogs don't have a mere two eyelids—they have three. While your dog may blink with two eyelids, just like we do, they also have a third lid, called a nictitating membrane or a haw, which moves horizontally across the eye from the inside corner.

Dogs Eye Anatomy Everything You Need To Know About Them Zigzag
Considering the physiology of the dog eye discussed above, and the dim light conditions to which it is adapted, dogs may be more sensitive to light at the expense of being able to discriminate smaller details.. Miller's Anatomy of the Dog: Elsevier Health Sciences. Feng, L. C., Chouinard, P. A., Howell, T. J., & Bennett, P. C. (2016). Why do.
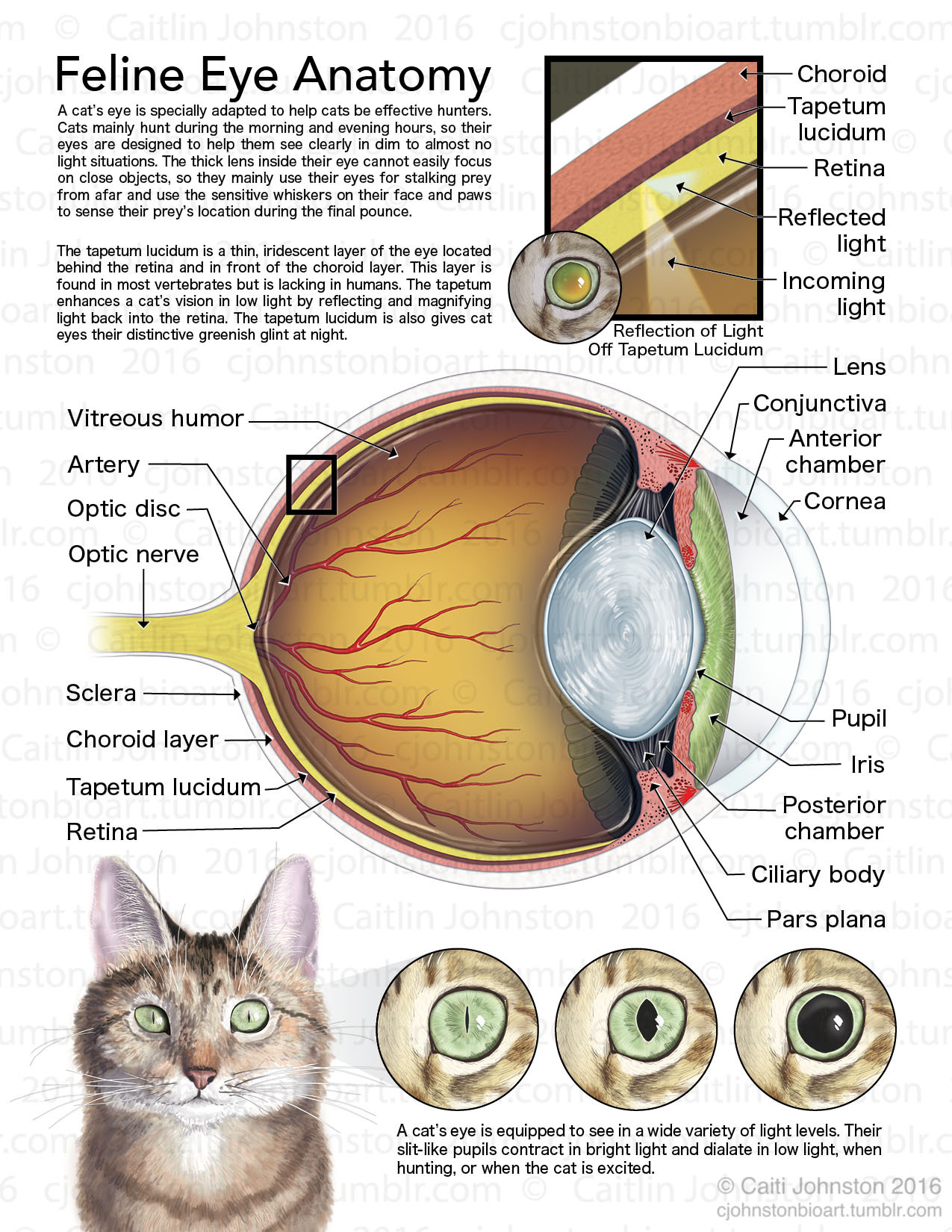
Scientific Illustration cjohnstonbioart Feline Eye Anatomy (2016)
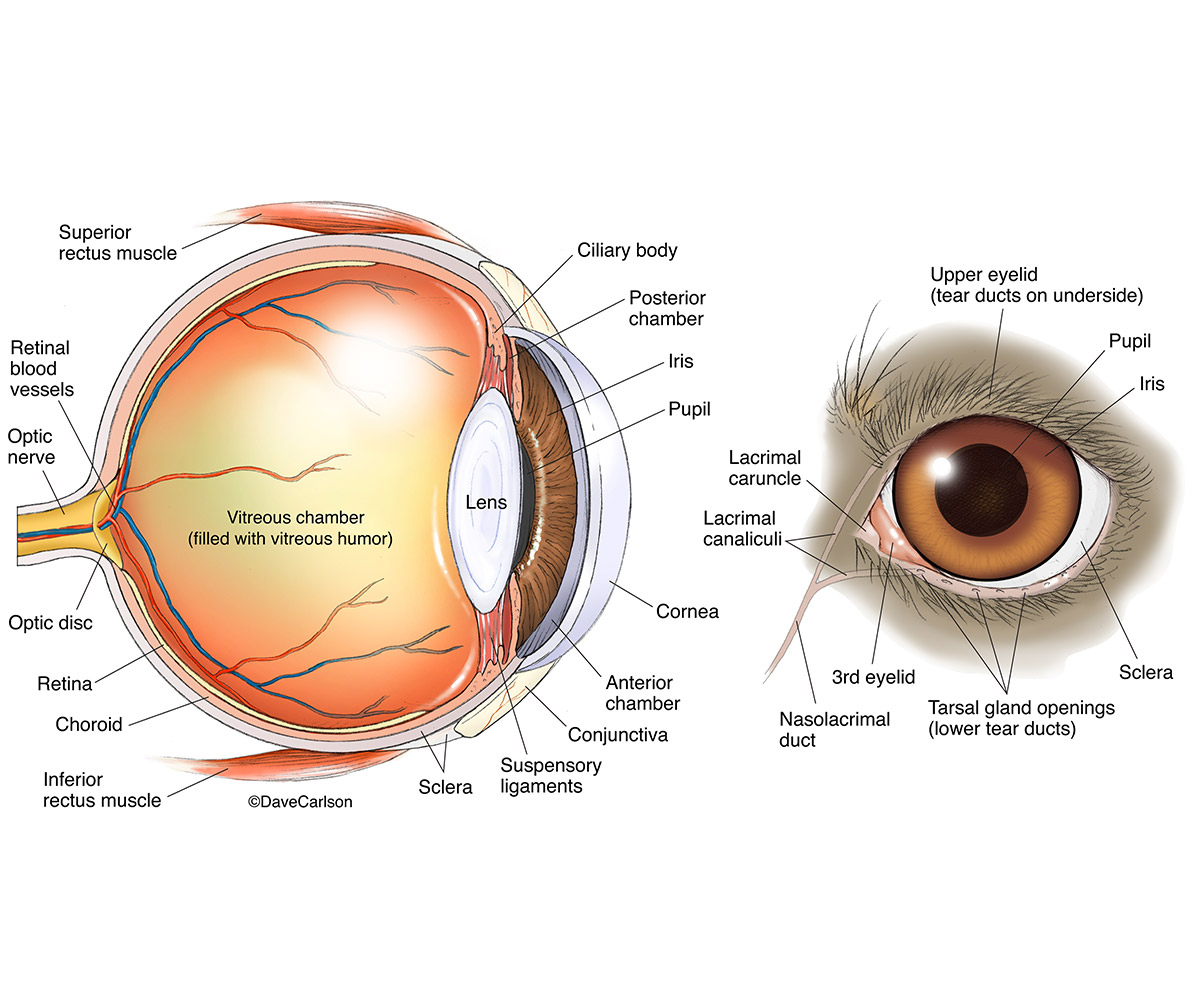
Dog Eye Anatomy " Dog Eye Anatomy is a reflection of the eye as a complicated organ, containing many parts. These functional parts, i.e. sclera, conjunctiva, cornea, iris, pupil, lens, retina, lacrimal gland etc. are contained in a bony socket called a "orbit".

Why are my dog's eyes goopy? — VAH
General Anatomy. Dogs generally have the same anatomical structure as humans [2] Dogs have a third eyelid, called the nictitating membrane, which further protects the eye, spreads tearfilm over the cornea, and is involved in tear production. [2] Dogs have a tapetum lucidum behind the retina, which is highly reflective, and increases night vision.
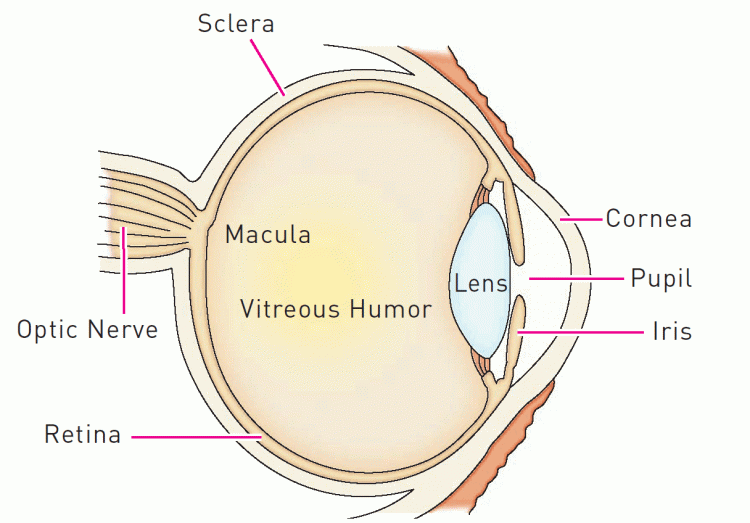
Dog Eye Anatomy Third Eyelid dogjullle
Pet Eye Disease EYE ANATOMY AND DISEASE MASTER CLASS™ Introduction Vision is one of the five senses along with taste, smell, hearing, and touch. The eyes are direct extensions of the brain, receiving visual information and processing it to give a stereoscopic view of the world.

Dog eye anatomy explained Brookfield Animal Hospital
Dog Vision: Understanding Canine Eye Anatomy Dogs' eyes are structurally very similar to human eyes. The colored part is the iris, which surrounds the dark round pupil and controls how much light passes through that opening.

Pin by Deborah on Painting Dog portraits painting, Animal paintings, Animal drawings
The act of "seeing" is a complex process that depends on (1) light from the outside world falling onto the eye, (2) the eye efficiently transmitting and properly focusing the images of these objects on the retina, (3) the retina detecting these light rays, (4) transmission of this information via the visual pathways to the brain, and (5) the bra.

What Is Cherry Eye In Dogs? CohaiTungChi Tech
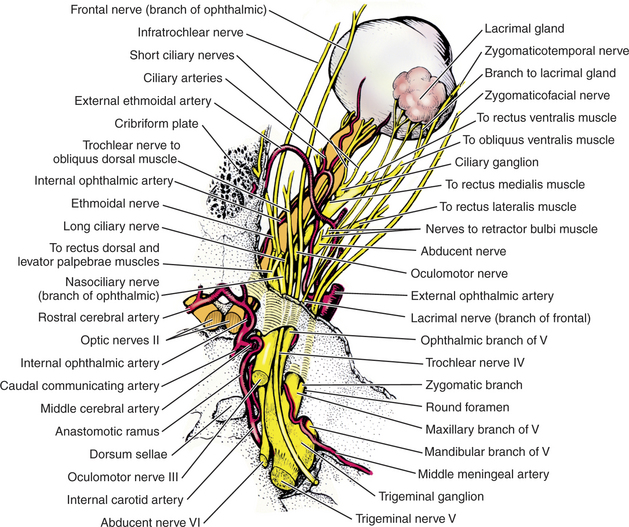
The eye ( organum visus) (Fig. 21-1) develops as a neuroectodermal outgrowth of the embryonic prosencephalon that contacts surface ectoderm and is enveloped by induced mesodermal and neural crest mesenchyme. The definitive eye and its adnexa are contained within an orbit that is only partly bony.

lacrimal caruncle Google 검색 Eye anatomy, Dog eyes, Cherry eye in dogs
Understanding Dog Eye Anatomy Dogs Zoology · Follow 2 min read · Aug 1 The fascinating world of canine eye anatomy must be explored as we set out on our adventure to preserve the vision of.

All About Your Dog's Eyes
The dog eye anatomy includes eyeball, orbit, eyelid, and lacrimal apparatus. This article will help you to know the details of these structures from the dog eye with labeled diagrams. Quick overview: The eyeball of a dog eye is located in the orbital cavity and consists of 3 tunics - fibrous, vascular, and nervous.
.png)
Dry Eye/KCS Little Critters Veterinary Hospital Gilbert, AZ
The anatomy of a dog's eye is very similar to that of a human's, though vision differs greatly. Cornea: A thin, smooth, transparent layer at the front of the eye. Trauma, ulceration, and irritating chemicals can lead to changes in the clarity of the cornea. Sclera: The "whites of the eyes."

Pet Eye Disease, Dog Eye Anatomy And Structure Guide Safarivet
The anatomy of dogs' and cat's eyes work by adjusting to different light conditions essential for hunting or tracking prey. Important Structures of the Eye The orbit is the bony cavity or socket which holds the eyeball as well as muscles, nerves, blood vessels, and structures that produce and drain tears.